The ‘Does It Fly?’ podcast separates fact from science fiction
The podcast ‘Does It Fly?’ asks whether the technology of Star Trek, Doctor Who and other popular sci-fi shows could really work.
Every print subscription comes with full digital access

Political scientists disagree over how to interpret a slight dip in the health of U.S. democracy.

The podcast ‘Does It Fly?’ asks whether the technology of Star Trek, Doctor Who and other popular sci-fi shows could really work.

The Florida Current, a major contributor to a system of ocean currents that regulate Earth’s climate, has not weakened as much as previously reported.
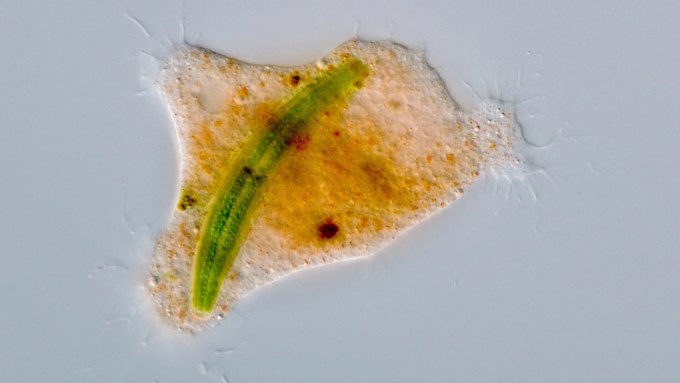
Meet the ‘owl slime’ amoeba, which drains its prey and spits out the shell.

Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.

Cosmological data suggest unexpected masses for neutrinos, including the possibility of zero or negative mass.

Brain scans revealed that teenagers with larger attention-driving networks were more likely to develop depression.

A study of people with type 2 diabetes and opioid use disorder suggests that the key ingredient in Ozempic and Wegovy shows promise against addiction.

Black garden ants made tweaks to entrances, tunnels and chambers that may help prevent diseases from spreading.
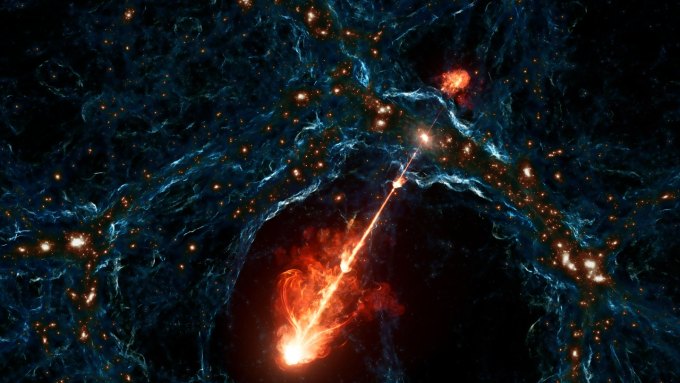
The two plasma fountains, spanning 23 million light-years, could shape cosmic structures far beyond their home galaxy.

With explosive bursts of pollen, male Hypenea macrantha flowers knock some competitors’ deposits off hummingbird beaks before the birds reach females.

A timeline of 485 million years of Earth’s surface temperatures shows ancient greenhouse conditions were hotter than scientists thought.

Flybys of primordial black holes may occur once a decade. Tweaks to the orbits of planets and GPS satellites could give away their presence.
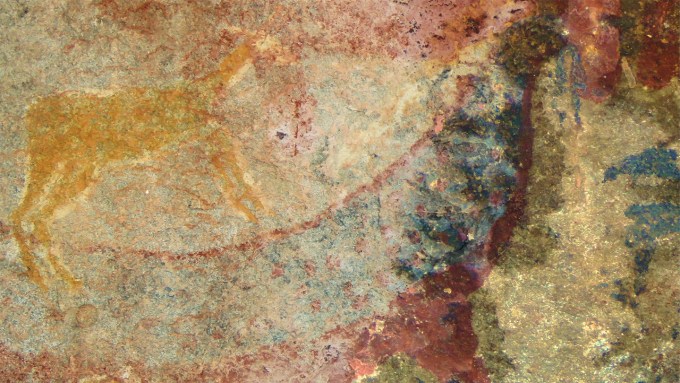
Unusual tusks on preserved skulls of dicynodonts influenced the look of a mythical beast painted by Southern Africa’s San people, a researcher suspects.

Long-lasting, widespread heat and weather extremes may have caused the Great Dying extinction event 252 million years ago.

If the pluripotent stem cells can be turned into precursors to egg and sperm cells, the feat could potentially be a big deal for giant panda conservation.
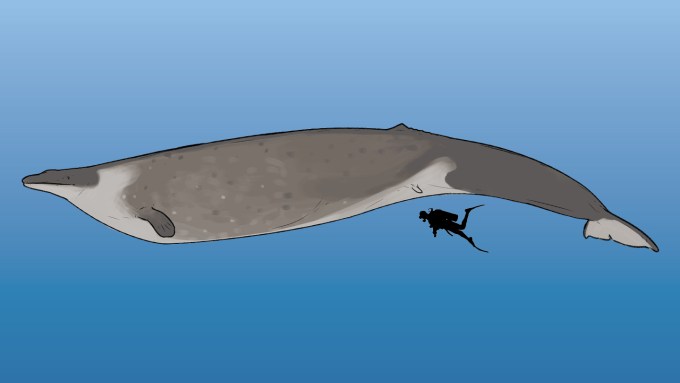
Evolving techniques and data indicate some ancient giants like Dunkleosteus and Megalodon may have been smaller than initial estimates suggested.

When inhaled, metals left by the shrinking lake could cause inflammation. Experts say more studies are needed to understand the impact.

A long-standing idea of why lithium ion batteries die focuses on lithium movement into the cathode. Instead, hydrogen may be to blame.

The “golden channel” decay of subatomic particles called kaons could break or confirm the standard model of particle physics.

Top quarks and antiquarks produced in the Large Hadron Collider are entangled, a study shows.
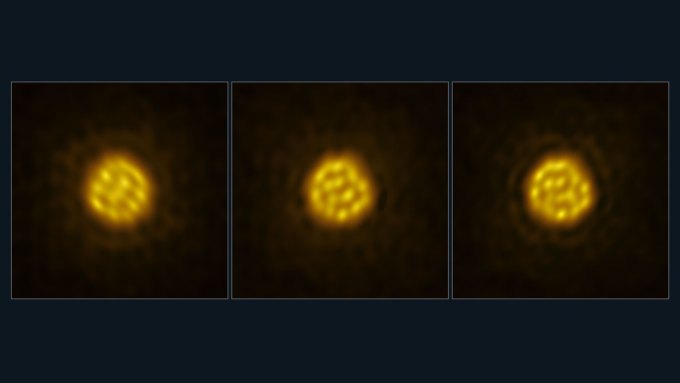
In a first, astronomers captured how convective forces power the quick bubbling movement of gas cells on the surface of a distant, massive star.
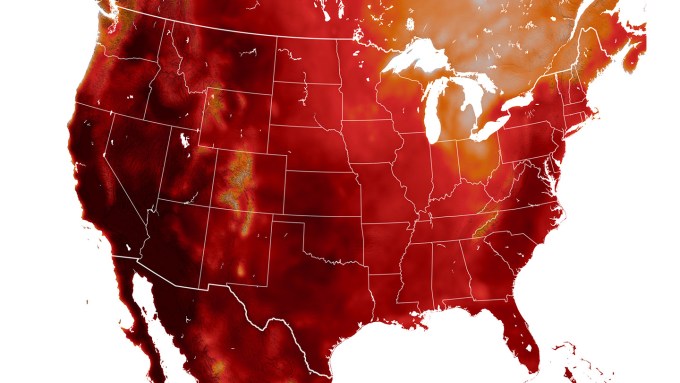
Each year, roughly 8,000 deaths in the United States are associated with extreme temperatures. And as temperatures rise, this number could swell.

A new computer program adjusts grow lights to cut down on electric bills without sacrificing photosynthesis.

Animals including mammals usually protect their brains from infiltrating microbes that can cause disease. But some fish seem to do just fine.
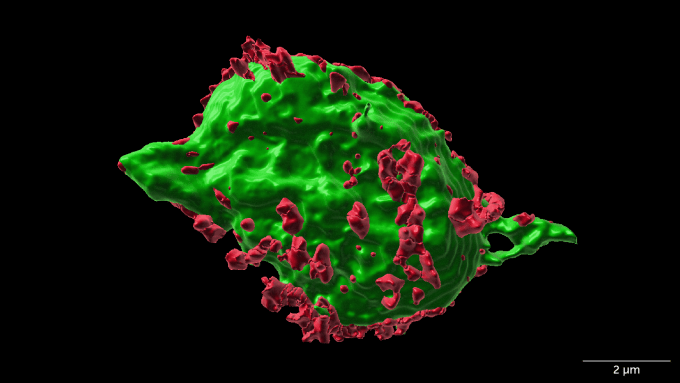
The finding suggests that a drug to ease swelling can speed recovery and stop cell death.

Chronic pain has puzzled scientists for decades, but diagnoses and treatments have come a long way.
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address to access the digital replica edition.